[ad_1]
Scientists at Rice University have developed synthetic protein switches to control the flow of electrons.
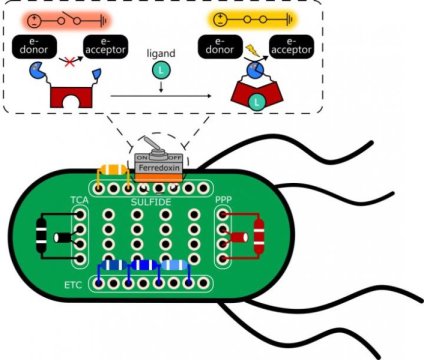
The proof-of-concept, metal-containing proteins made in the Rice lab of synthetic biologist Joff Silberg are expressed within cells upon the introduction of one chemical and are functionally activated by another chemical. If the proteins have been placed in the cell, they can simply be turned on and off.
“This is not a metaphor for a switch, it is a literal electrical switch built from a protein,” Silberg said.
The proteins could facilitate next-generation bioelectronics, including complete biological circuits within cells that mimic their electronic counterparts. The possible applications include living sensors, electronically controlled metabolic pathways for chemical synthesis and active pills that sense their environment and release drugs only when needed.
The work appears in Nature Chemical Biology. “Biology is really good at sensing molecules,” said Silberg, a professor of biosciences and bioengineering. “That’s an amazing thing. Think about how complex the cell is, and how proteins evolve that can respond to a single prompt in a sea of information. We want to leverage that exquisite ability to build more elaborate biomolecules and use these to develop useful synthetic biology technologies.”
The Rice team takes advantage of those innate abilities. “Natural proteins that move electrons more or less act as wires that are always there,” said Systems, Synthetic, and Physical Biology graduate student and lead author Josh Atkinson. “If we can turn these pathways on and off, we can make cells operate more efficiently.”
Rice’s metalloprotein switches — so called for their iron content — are quick, Silberg said. Nature typically controls electron flow by using genetic mechanisms to control the production of the protein “wires.”
“It’s all transcriptional,” he said. “Even in a fast-growing E. coli bacteria, it takes many minutes. By contrast, protein switches function on a time scale of seconds.”
To make the switch — which they use in a synthetic electron transfer pathway — the researchers needed a stable protein that could be reliably split along its peptide backbone to allow for the insertion of protein fragments that complete or break the circuit. They based the switch on ferredoxin, a common iron-sulfur protein that mediates electron transfer in all the domains of life.
Atkinson built switches embedded in E. coli that can be turned on in the presence (or off in the absence) of 4-hydroxytamoxifen, an estrogen receptor modulator used to fight breast and other cancers, or by bisphenol A (BPA), a synthetic chemical used in plastics.
Their E. coli bacterium is a mutant strain that is programmed to only grow in a sulfate medium when all of the components of the ferredoxin electron transport chain — including electron donor and acceptor proteins — are expressed. That way, the bacteria could only grow if the switches turn on and transfer electrons as planned.
Silberg said the discovery should lead to custom-designed switches for many applications, including contact with external electronic devices. “It’s why we’ve been so gung-ho about this idea of bioelectronics, a whole field that’s emerging as synthetic biology gets more control over the design,” he said. “Once you can standardize this, there are all kinds of things we can build with cells.”
That could include smart pills that release medications only on demand, or gut biome detectors that report on conditions. Or perhaps electrical circuits contained entirely within cells.
“We can already map a lot of what electrical engineers do with capacitors and resistors onto metabolism, but until now, there have been no switches,” Silberg said.
He suggested multiple switches could also turn a cell into a biological processor. “Then we could see digital parallel processing in the cell,” he said. “It changes the way we look at biology.”
Story Source:
Materials provided by Rice University. Note: Content may be edited for style and length.
[ad_2]