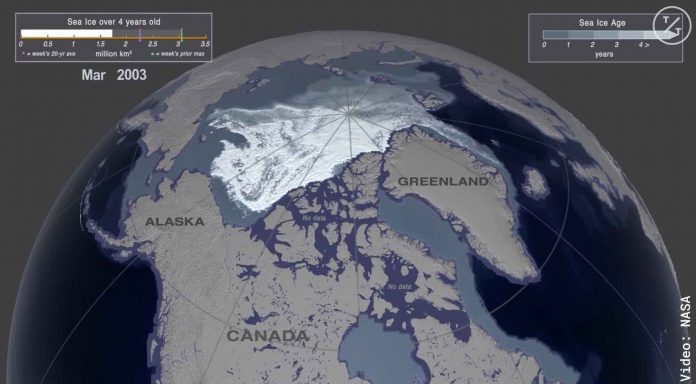
In the 1st week of January 1988, over 1.2 million sq. miles were covered by sea ice 4 years of age or older, compared with just over 44,000 sq. miles in the same week in 2019.
Perennial sea ice is the portion of the sea ice that survives the summer melt season. Perennial ice represents the thickest component of sea ice and can grow up to four meters thick, NASA said. Ice that grows during a single winter is generally two meters thick or less.
In this visualization, younger sea ice is shown in a shade of blue while ice that is four years old or older is shown in white. A graph in the upper left quantifies the area covered by sea ice that is four or more years old.
The area of ice cover drops dramatically during the 35-year period.
NASA said that in the first week of January 1988, 3,121,000 square kilometers were covered by sea ice four years of age or older, compared with just 116,000 square kilometers in the same week in 2019.