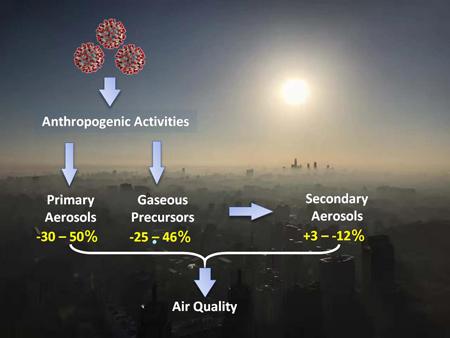
IMAGE: Changes in primary aerosols, gaseous precursors, and secondary aerosols during the COVID-19 outbreak and Chinese New Year holiday.
view more
Credit: Hao Li
The novel coronavirus disease (COVID-19) spreads rapidly around the world, and has limited people’s outdoor activities substantially. Air quality is therefore expected to be improved due to reduced anthropogenic emissions. However, in some megacities it has not been improved as expected and severe haze episodes still occurred during the COVID-19 lockdown.
A research team led by Prof. Yele Sun from the Institute of Atmospheric Physics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences analyzed six-year aerosol particle composition measurements to investigate responses of air quality to the changes in anthropogenic emissions during the COVID-19 outbreak in Beijing, China, as well as the Chinese New Year holiday effects on air pollution.
They found that air pollution during the COVID-19 lockdown was mainly due to different chemical responses of primary and secondary aerosols to changes in anthropogenic emissions.
“Primary gaseous and aerosol species responded directly to emission changes and decreased substantially by 30-50%”, said Sun. “However, secondary aerosol species that are formed from oxidation of gaseous precursors and accounted for more than 70% of particulate matter remained small changes of less than 12%. Therefore, fine particle pollution hasn’t been improved as expected.”
The air quality in Beijing has been improved during the last decade, and the mass concentrations of both primary and secondary pollutants decreased considerably.
However, according to this new study published in Sci. Total Environ, the increased sulfur and nitrogen oxidation capacity have suppressed the effects of emission reductions due to enhanced secondary formation.
These findings highlight a great challenge for mitigating secondary air pollution in regions with a cocktail of high concentrations of gaseous precursors.
“There’s an urgent need for a better understanding of the chemical interactions between precursors and secondary aerosol under complex meteorological environments,” said Sun.
###
TDnews














