IMAGE: Study authors compare the physiology of a pediatric lung and an adult lung.
view more
Credit: Photo credit: Krithika Lingappan, MBBS; Matthew Harting, MD; Bindu Akkanti, MD
Differences in lung physiology and immune function in children could be why they are more often spared from severe illness associated with COVID-19 than adults, according to pediatric and adult physicians at The University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston (UTHealth) and Baylor College of Medicine, who teamed up to investigate the disparity.
The perspectives paper was recently published in American Journal of Physiology-Lung Cellular and Molecular Physiology.
According to the paper, only about 1.7% of the first 149,082 cases in the U.S. were infants, children, and adolescents younger than 18 years old. Authors noted that children under 18 make up 22% of the U.S. population. Only three pediatric deaths were identified by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) as of April 2020.
“These profoundly decreased rates of symptomatic infection, hospitalization, and death are well beyond statistical significance, require further examination, and may hold the key to identifying therapeutic agents,” the authors wrote.
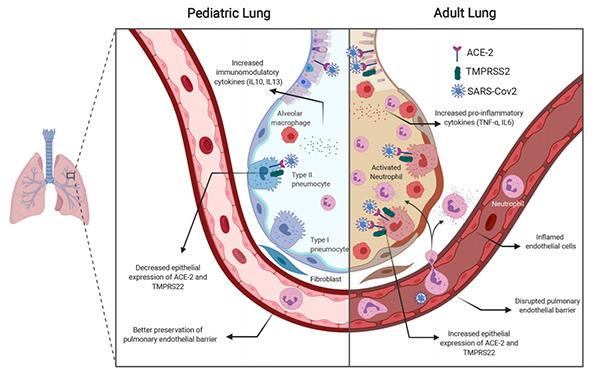
Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2s, called ACE2, are the doors that allow SARS-CoV-2, the novel coronavirus that causes COVID-19, to enter the body’s cells. Children naturally have less ACE2 in the lungs than adults.
“ACE2 are important for viral entry and there seems to be less of them in children, because they increase with age,” said Matthew Harting, MD, MS, assistant professor in the Department of Pediatric Surgery at McGovern Medical School at UTHealth, pediatric surgeon with UT Physicians, and senior author of the paper. Harting is also director of the pediatric ECMO program providing advanced cardiac and respiratory support at Children’s Memorial Hermann Hospital.
In addition to fewer ACE2 receptors, the authors note the immune system in children responds to viruses differently than that of adults, leaving less opportunity for severe illness in pediatric patients. There are several different mechanisms behind the differences, including the retention of T-cells in children, which are able to fight off or limit inflammation.
“T-cells have a viral response and also an immune modulator response. In severe cases of adult COVID-19 patients, we’ve seen that those T-cells are reduced, so the ability to fight the virus is also reduced. In kids, those T-cells seem to be maintained, so they are still able to prevent the virus,” said Harry Karmouty-Quintana, PhD, an assistant professor in the Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology at McGovern Medical School, and a co-author of the paper.
Lung tissue in children naturally has a higher concentration of regulator T-cells. Patients with higher levels of T-cells also have higher levels of Interleukin 10 (IL-10), also known as human cytokine synthesis inhibitory factor, an anti-inflammatory cytokine.
“IL-10 inhibits the inflammation of other components like IL-6 that are detrimental. Adults tend to experience hyperinflammatory state, where kids do not,” Karmouty-Quintana said. “In preclinical studies in mice, IL-10 has also shown to decrease with age.”
The paper’s findings were made possible through collaboration in a multidisciplinary group made up of pediatric and adult physicians and scientists in pediatric surgery, adult critical care, neonatology, and molecular biology.
“We, as physicians, have been challenged with the question of how to treat COVID-19 and we’re learning in real time,” said Bindu Akkanti, MD, associate professor of critical care medicine with McGovern Medical School, attending physician in critical care with Memorial Hermann-Texas Medical Center, and a study co-author. “I knew that to figure out the best way to treat adults, we needed to get a team together to get to the bottom of why children were being spared from severe illness related to the virus. So, I reached out to Dr. Karmouty-Quintana and we teamed up with Dr. Harting and two other physicians in the Texas Medical Center to start investigating.” Akkanti also sees pulmonary patients at UT Physicians.
“Collaborations like this between adult and pediatric providers are really important and this disease highlights where we can learn a lot when we compare the way it behaves in younger kids with older people,” Harting said. “Even now as we’re learning about effective treatments, we’re seeing younger people handle this disease better than older people. Moving forward, physicians and scientists need multidisciplinary collaboration to continue learning – this is just another step in the right direction to attack this virus.”
Krithika Lingappan, MBBS, was the first author of the paper and Jonathan Davies, MD, was a co-author. Both Lingappan and Davies are assistant professors of pediatrics at Baylor College of Medicine and neonatologists with Texas Children’s Hospital.
As a result of the collaboration, the team has begun a new study using blood samples from patients in different stages of COVID-19 to continue to understand how to treat the virus and the disparities in disease progression between children and adults.
###
TDnews














